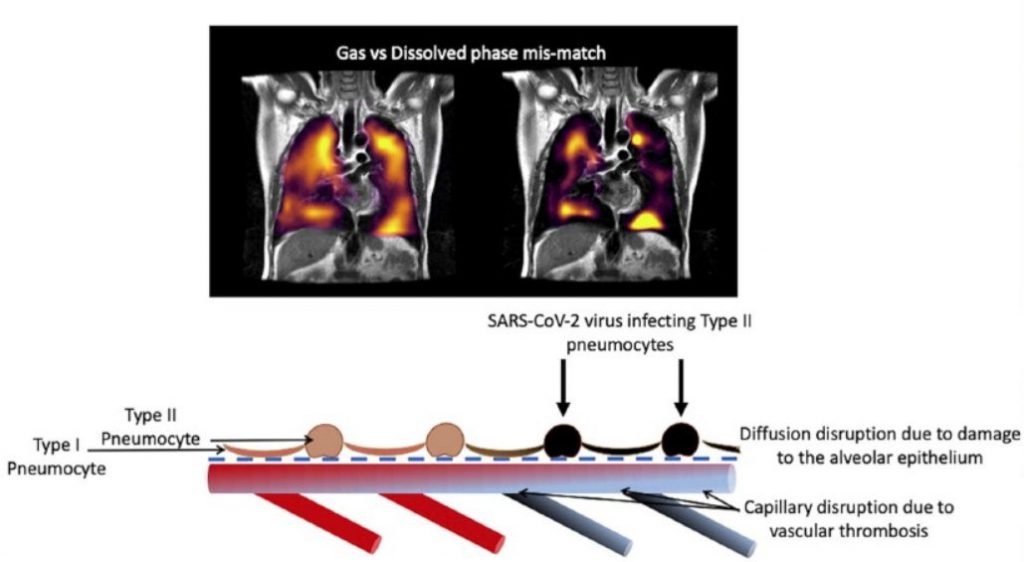
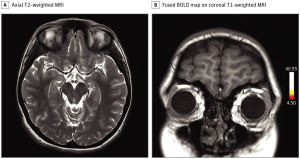
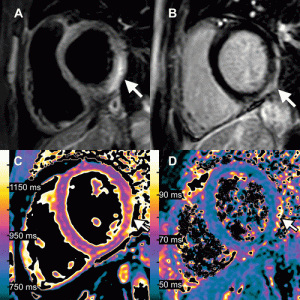
Sheffield and Oxford researchers used a cutting-edge method of MRI imaging technique based on the hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI (XeMRI) for studying the lungs of COVID-19 patients at least three months after they were discharged from hospital, and for some patients even longer. They showed abnormalities due to gas transfer limitation in the lungs of these patients who were experiencing shortness of breath three months after being discharged from the hospital for COVID-19 pneumonia. This result is interesting as their CT scans indicating that their lungs are functioning normally.